super class i occlusion
The relation between the surfaces when in contact. This classification is used when the upper front teeth protrude out past the lower front teeth.
1 Orthodontic Diagnosis And Treatment Planning Pocket Dentistry
Definition of occlusion.
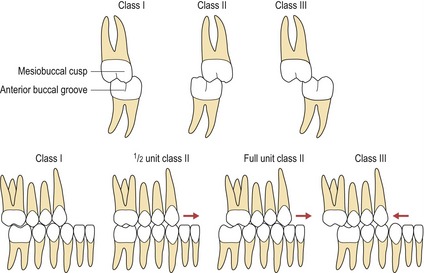
. The complete obstruction of the breath passage in the articulation of a speech sound. A Class 3 molar relationship is described as. This classification refers to the position of the first molars and t he way in which the upper ones fit together with the lower ones.
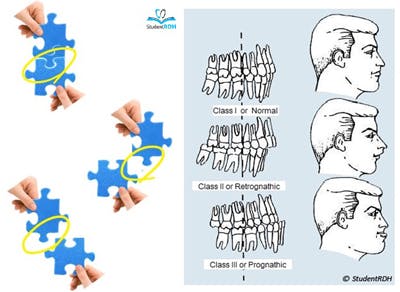
Each class can also become more specific by being. He based his classifications on the relative position of the permanent MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR. The red line is Angles line of occlusion and any Class I occlusions with deviations to this line are defined as a Class I malocclusion.
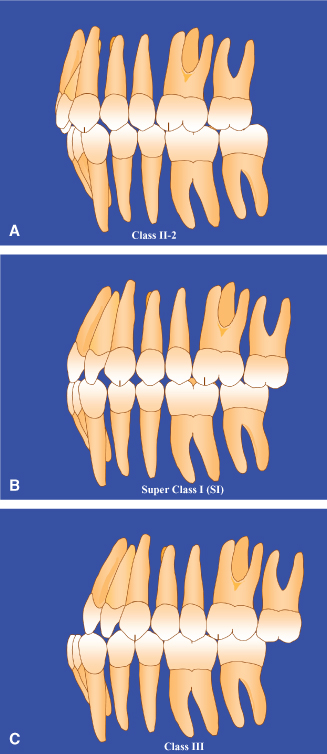
A malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the two dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. Class I pseudo-Class I super Class I. Refers to the contact relationship between the maxillary and mandibular teeth when the jaws are in a fully closed position.
Occlusion is an integral part of dental treatment as dentists cannot repair move or remove teeth without affecting occlusion. Class 1 dental malocclusion is the most common type of malocclusion. This is the most common out of the three dental occlusion classes.
This is important because the classification of the bite also indicates whether there is a skeletal discrepancy. Also known as prognathism this class of malocclusion occurs when the lower front teeth are more prominent than the upper front teeth and the patient has a large lower jaw or a short upper one. Which is it and why is it important.
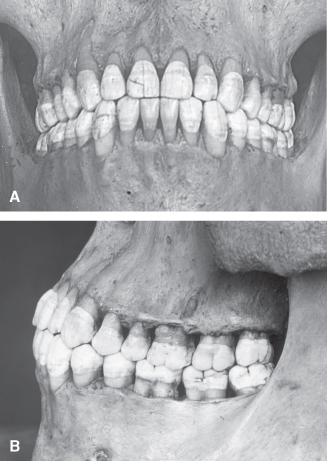
Class 1 Malocclusion Neutrocclusion This is the most common type of malocclusion in which the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth. The bringing of the opposing surfaces of the teeth of the two jaws into contact also. The mesiobuccal cusp of the upper first molar occludes with the buccal groove of the lower first molar.
Approximately 50 to 55 of children between the ages of 6 and 17 have some form of Class 1 malocclusion. In this case the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary. Type 2 occurs when the upper front teeth alignment is good but the lower front teeth angle toward the tongue.
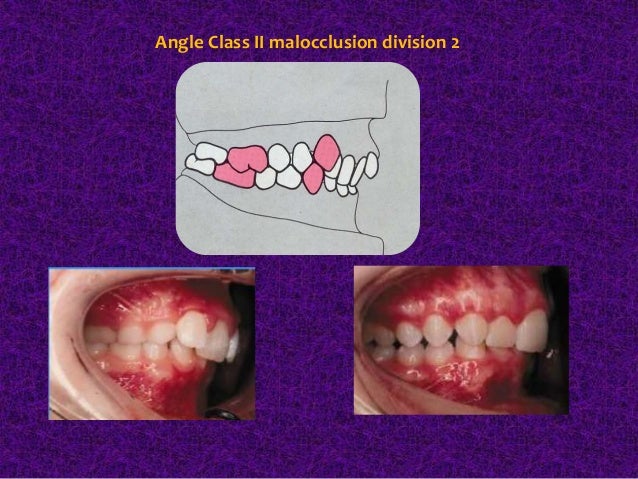
The first of the six keys is molar. The three classes according to Angles classification are as follows. The American Veterinary Dental College defines Class II malocclusion as mandibular distocclusion when there is an abnormal rostro-caudal relationship between the dental arches in which the mandibular arch occludes caudal to its normal position relative to the maxillary arch Figure 3Terms that have commonly been associated with class II.
The mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar occluding posterior to the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar ie. Maxillary marginal ridges and central fossae of. Andrews in 1972They have significant clinical implications for routine orthodontic therapyFurther ReadingAndrews L.
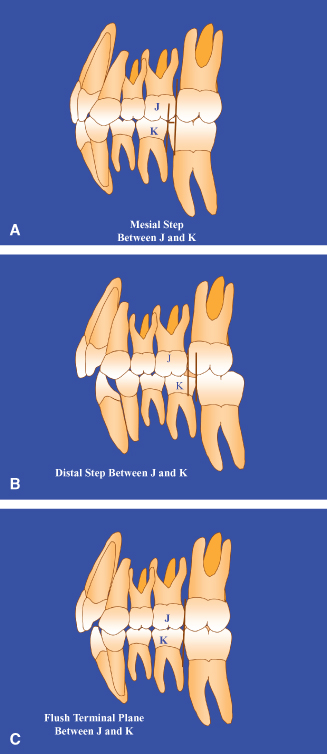
The voluntary position of the dentition that allows for maximum contact when the teeth occlude. There is normal relationship of the molars but the line of occlusion is incorrect because of malposed teeth rotations or other causes. There are three types of Class 3 malocclusions.
The articulatory system is in itself a triumvirate comprising the. Edward Angle who is considered the father of modern orthodontics was the first to classify malocclusion. Classification of the bite occlusion is divided into three main categories.
The six keys to normal occlusion contribute individually and collectively to the total scheme of occlusion and therefore are viewed as essential to successful orthodontic treatment. Within these three classes there are seven different types of misalignment a patient can have. The plane of occlusion varied from generally flat to a slight curve of Spee.
This class includes underbites and crossbites. The masticatory system comprises the teeth the periodontal tissues and the articulatory system. The cusp tip of the upper cuspid is forward of the lower cuspid.
Class I pseudo-Class I super Class I. The bite however is normal. Type 3 is when the lower teeth alignment is okay but.
The green line is the Esthetic line or. For a perfect occlusion the cusp of the upper first molar should rest in the groove of the lower first molar. Class II malocclusion D.
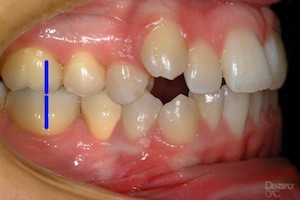
Class I II and III. However your other teeth may have gaps andor are crowded. Class 1 is when your upper teeth overlap with your lower teeth but in a manageable position.
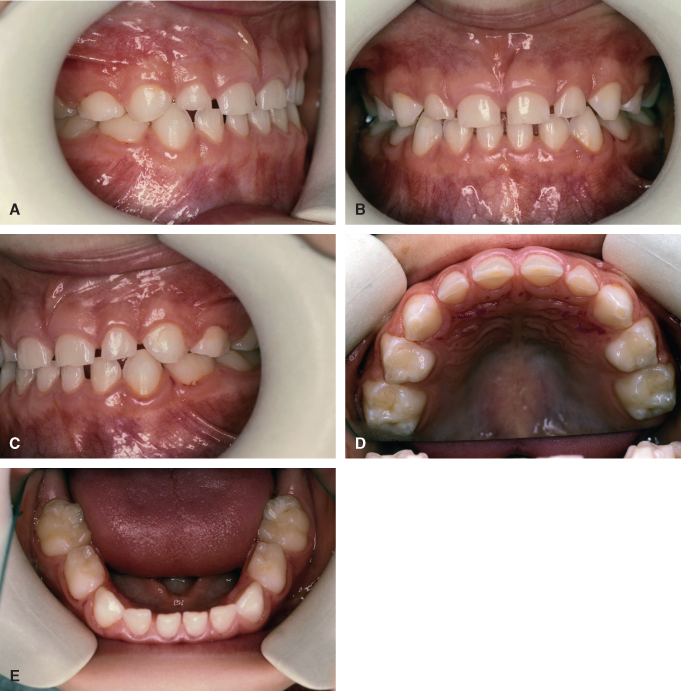
Lateral view of occlusion pretreatment A and at the end of distal movement of Tooth 26 when a super Class I relationship had been achieved B. To solve the question first identify the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar and see if it fits in the mesiobuccal groove of the mandibular first molar. The act of occluding.
Dental malocclusions are classified based on the positioning of the upper and lower molars. Class II malocclusion. The state of being occluded.
The maxillary first molar is severely posteriorly positioned relative to the mandibular first molar. Type 1 is when the arch of the teeth has an abnormal shape but the alignment is good. Class I pseudo-Class I super Class I.
Unlike a class II malocclusion the lower teeth overlap the upper teeth and jaw. Class III in this form of malocclusion the lower jaw is pushed forward. After Herbst treatment T2 a bilateral Class I or super Class I 025 cusp widths mesial molar relationship was seen in 182 of the subjects of the SYM subjects only.
The dental term of this protrusion is overjet. Class I malocclusion C. A class 1 malocclusion means that the molar position or bite is normal but.
Same as normal occlusion but characterized by crowding rotations and other positional irregularities. The upper first molar cusp lines up forward of the developmental groove of the lower first molar. Class II in this form of malocclusion the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth and jaw.
All the other teeth should also fall in the line of occlusion.
1 Orthodontic Diagnosis And Treatment Planning Pocket Dentistry

Dentaltown Where The Dental Community Lives Dental Hygiene School Dental Hygiene Student Dental Assistant Study

1 056 Likes 9 Comments Dentistry Today Dentistry2day On Instagram All Class Restorat Anatomia Dental Escola De Higiene Dental Odontologia Restauradora

Malocclusion Bite Patterns C Youtube
Angle S Classification For Malocclusions Dentalnotebook
1 Orthodontic Diagnosis And Treatment Planning Pocket Dentistry
Occlusion And Malocclusion Pocket Dentistry

Dental Ergonomics How To Access Patient S Teeth In The Different Quadrants Clock Positioning Dental Cosmetic Dentistry Dental Assistant School Dental Anatomy

Startrader Class Super Freighter Super Class Startrader Space Spaceship Design 3d Model Model
1 Orthodontic Diagnosis And Treatment Planning Pocket Dentistry
Bite Classification Petaluma Orthodontics Petaluma Ca

Must Know Classifications Of Dental Caries For The National Dental Hygiene Boards Dental Caries Dental Dental Hygiene School
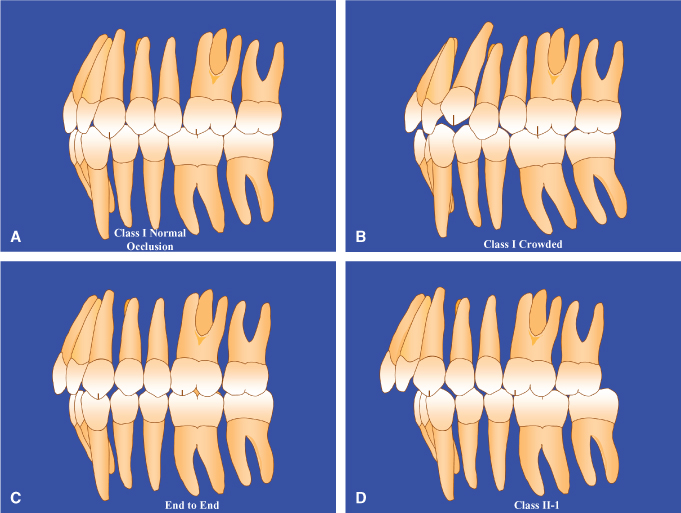
1 Orthodontic Diagnosis And Treatment Planning Pocket Dentistry

Root Morphology Anatomy Dental Anatomy Registered Dental Hygienist Dental Hygiene Student

Treatment Of A Severe Class Ii Division 1 Malocclusion Combined With Surgical Miniscrew Anchorage American Journal Of Orthodontics And Dentofacial Orthopedics

Dental Charting Symbols World Of Template Format Throughout Dental Charting Symbols24166 Dental Charting Dental Hygiene Student Dental Hygiene School

Remove And Implant Vs Retain And Restore Implants Dentistry Spear Education

Classifying Occlusion Board Exam Tips From Studentrdh Com Dentistry Iq
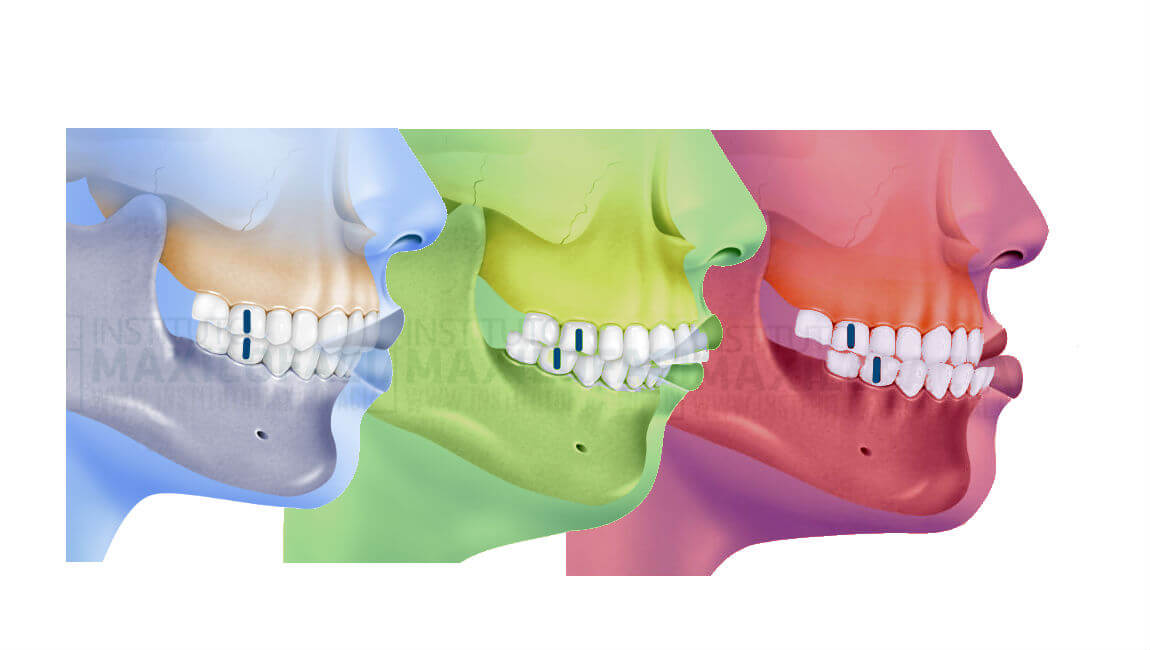
What Is A Class I Class Ii Or Class Iii Bite Instituto Maxilofacial